
Sophos, a global leader in next-generation cybersecurity, today released the “Active Adversary Playbook 2021,” detailing attacker behaviors and the tools, techniques and procedures (TTPs) that Sophos’ frontline threat hunters and incident responders saw in the wild in 2020. The TTP detection data also covers early 2021. The findings show that the median attacker dwell time before detection was 11 days – or 264 hours – with the longest undetected intrusion lasting 15 months. Ransomware featured in 81% of incidents and 69% of attacks involved the use of the remote desktop protocol (RDP) for lateral movement inside the network.
The playbook is based on Sophos telemetry as well as 81 incident investigations and insight from the Sophos Managed Threat Response (MTR) team of threat hunters and analysts and the Sophos Rapid Response team of incident responders. The aim is to help security teams understand what adversaries do during attacks and how to spot and defend against malicious activity on their network.
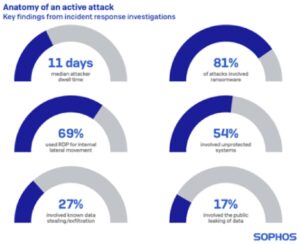 Key findings in the playbook include:
Key findings in the playbook include:
- The median attacker dwell time before detection was 11 days – To put this in context, 11 days potentially provide attackers with 264 hours for malicious activity, such as lateral movement, reconnaissance, credential dumping, data exfiltration, and more. Considering that some of these activities can take just minutes or a few hours to implement – often taking place at night or outside standard working hours – 11 days offers attackers plenty of time to cause damage in an organization’s network. It is also worth noting that ransomware attacks tend to have a shorter dwell time than “stealth” attacks, because they are all about destruction
- 90% of attacks seen involved the use of the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) – and in 69% of all cases, attackers used RDP for internal lateral movement – Security measures for RDP, such a VPNs and multi-factor authentication tend to focus on protecting external access. However, these don’t work if the attacker is already inside the network. The use of RDP for internal lateral movement is increasingly common in active, hands-on-keyboard attacks such as those involving ransomware
- Interesting correlations emerge among the top five tools found in victim networks. For instance, when PowerShell is used in an attack, Cobalt Strike is seen in 58% of cases, PsExec in 49%, Mimikatz in 33%, and GMER in 19%. Cobalt Strike and PsExec are used together in 27% of attacks, while Mimikatz and PsExec occur together in 31% of attacks. Lastly, the combination of Cobalt Strike, PowerShell and PsExec occurs in 12% of all attacks. Such correlations are important because their detection can serve as an early warning of an impending attack or confirm the presence of an active attack
- Ransomware was involved in 81% of the attacks Sophos investigated. The release of ransomware is often the point at which an attack becomes visible to an IT security team. It is, therefore, not surprising that the vast majoirty of the incidents Sophos responded to involved ransomware. Other attack types Sophos investigated included exfiltration only, cryptominers, banking trojans, wipers, droppers, pen test/attack tools, and more
“The threat landscape is becoming more crowded and complex, with attacks launched by adversaries with a wide range of skills and resources, from script kiddies to nation-state backed threat groups. This can make life challenging for defenders,” said John Shier, Sophos Sr Research Scientist. “Over the last year, our incident responders helped to neutralize attacks launched by more than 37 attack groups, using more than 400 different tools between them. Many of these tools are also used by IT administrators and security professionals for their everyday tasks and spotting the difference between benign and malicious activity isn’t always easy.
“With adversaries spending a median of 11 days in the network, implementing their attack while blending in with routine IT activity, it is critical that defenders understand the warning signs to look out for and investigate. One of the biggest red flags, for instance, is when a legitimate tool or activity is detected in an unexpected place. Most of all, defenders should remember that technology can do a great deal but, in today’s threat landscape, may not be enough by itself. Human experience and the ability to respond are a vital part of any security solution.”
Other topics covered in the playbook include the tactics and techniques most likely to signpost an active threat and warrant closer investigation, the earliest signs of attack, the most widely seen stagers, threat types and malicious artefacts, the most prevalent adversary groups seen, and more.
















